Fiche Diversite Culturelle ✅
Diversities in the anglophone world
Many different types of things or being included in something : => the social, economic, ethnic or cultural diversity of a country A situation where there are many different ideas or opinions about something : => different political or religious ideas (Cambridge dictionary)
What is culture ?
Culture is one of the most complicated terms to defined, they are many definitions depending on approaches or theory (philosophy,sociology…) Culture characterizes the practices and lifestyle shared by some humans beings : language, religions , customs , art/music, food, clothes, sports, beliefs, attitudes… Culture always change/ on the move and depend on people. Culture can be transmitted, learn, borrowed and/or created (sociological definition)
Cultural stereotypes
Culture is very often define according to specific statements and representations which are not always true or which are incomplete. Categorize people depending on their genders / origins / attitudes.
The danger of culture
Of course the stereotypes can be sometimes funny but they are also many others stereotypes which can be very hurtful and very dangerous as well. The main problem is when people consider that their culture is the only one which is valid as oppose to the others culture (example : the notion of the Western culture).This is part of a tendency call ethnocentrism. Ethnocentrism : the tendency to consider that our culture is superior and the only valid one. That all the other culture are strange and inferior.
One of the many consequences of ethnocentrism, is the rejection of all the others culture groups which can lead to issue in daily life for example issues in the workplace / school / social life. This rejection can take various forms / shapes, negative feeling or attitude = prejudice / negative behaviors or actions = discrimination. Racism is an example of both prejudice and discrimination. And sometimes ethnocentrism can also lead to fear and hatred of people with other cultures/ origins = xenophobia
Definitions
Cultural diversity refers to a situation where there are different groups within a society who try to maintain and develop their cultural identities.
- a sociological reality : immigrants have come to settle in a host / receiving society (=almost all countries in the world are multicultural)
- a political program : cultural differences are officially preserved and promoted (Multiculturalism in Canada, in Australia)
- an ideology : cultural differences are valuable and should be preserved (different metaphors : multiculturalism, cultural mosaic, salad bowl…)
Salad bowl = refers to a juxtaposition or addition of various ingredients that keep their individual characteristics and qualities. When applied to a given society characterized by cultural diversity, you can see that people are able to keep their original ethnic culture.
Integration vs Assimilation
-
Integration : people are bale to adopt the cultural norms of the dominant group culture while maintaining their culture of origin => “The Salad Bowl” or “Mosaic” metaphors
-
Assimilation : people give up their culture of origin and adopt norms of the dominant culture => “The Melting Pot” metaphor
The Melting pot concept
The USA are often refer as a mixture or a melting pot of people from a wide variety of culture / religion / tradition / ideas… In 1908, this concept was invented by Israel Zangwill (title of a play) to describe the process of assimilation of immigrants coming to the USA.(affiche diapo) This concept rely on the idea that everyone who lives in USA can become a part of a larger that is uniquely American. People have left behind their original identity to become American.
Salad bowl vs Melting pot
The image of the Salad Bowl celebrate diversity because Americans culture are juxtapose like salad ingredients but do not mixed. The image of Melting Pot, we can see a mixture or blending of many different people who would become American.
Nowadays, the cultural trend in the US is cultural diversity (=salad bowl) and not assimilation (=melting pot).
Race / ethnicity
- Race = often linked to biology (people having common hereditary traits), but also linked to culture.
- Ethnicity = linked to culture (people having a common ancestry or sharing a cultural heritage)
But the two categories can overlap because a person may have multiple racial and ethnic backgrounds.
The colonial period (1607-1776)
- 1607 : first English colony in Jamestown, Virginia
- New England Puritans (=Pilgrims) : not really willing to welcome immigrants
- Middle colonies : more eager to welcome new immigrants
- 17th century : English, Scottish and German immigrants (in Pennsylvania), and forced migration of Africans (1619)
- 18th century : European immigrants and continuation of African slavery
The ‘old’ immigrants(1820-1890)
An influx of immigrants from Northern and Western Europe (British, Irish, Germans…) + Central Europe. They were farmers, artisans, skilled factory workers and perceived as ‘good’ immigrants : same culture, same values… They could easily adapt/assimilate to the WASP (White Anglo-Saxon Protestant) model = ‘Ethnic’ hierarchy
The ‘new’ immigrants (1890-1930)
Many immigrants from Southern and Eastern Europe: Italians, Poles, Greeks, Jews, Hungarians… Because of industrialization, great need for factory workers but most jobs were unskilled and badly paid. Israel Zangwill’s play The Melting Pot (1908) = the U.S. would mix all the different cultures to create a new American people -> ‘Bad’ immigrants -> Tensions and reactions of xenophobia
The Emergence of Nativism(19th-20th centuries)
Nativism appeared in reaction to the arrival of immigrants whose culture was not part of the WASP culture. Nativism comes from the word ‘Native’ (=the descendants from the settlers of the 13 colonies). An anti-immigration feeling : nativists opposed immigration and feared for the purity of the white race. Nativist movements : the Know-Nothings (against Irish Catholics), the Immigration Restriction League, the anti-Asian movements (→ the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 banning Chinese immigration) ->Restrictive immigration laws : Emergency Quota Act (1921)
The Americanization program(20th century)
A majority of people were against Europeans immigrants but also many who want them to assimilate to the American mainstream through the American program. People were taught English, American history, government and American customs. The objective was to assimilate these people.
The 4th wave of immigration : after 1965
Immigration seriously decline but everything change with the 1965 Immigration and Nationality act also known as “The Hart Celler Act”. That was an act which ended racial quotas. These laws implemented preferential categories based on Family relationship and job skills. These act mark a change for the American immigration policy. After 1970, Immigrants started coming from Asia(Corea/India) and also from Africa. After 1980, there was a new tendency, people started to arrive from Latin America. So the population started to diversify a lot with the emergence of new community and new minority coming in

In 2017 : 1/5 of the world’s immigrants lived in the U.S.

Some definitions
- Native-born : a U.S citizen at birth
- Foreign-born : NOT a U.S citizen at birth
- naturalized U.S citizens
- legal permanent residents (=green-card holders)
- temporary migrants
- humanitarian migrants (=asylum seekers)
- unauthorized migrants (=illegal/undocumented immigrants )
Legal / Illegal Immigrants
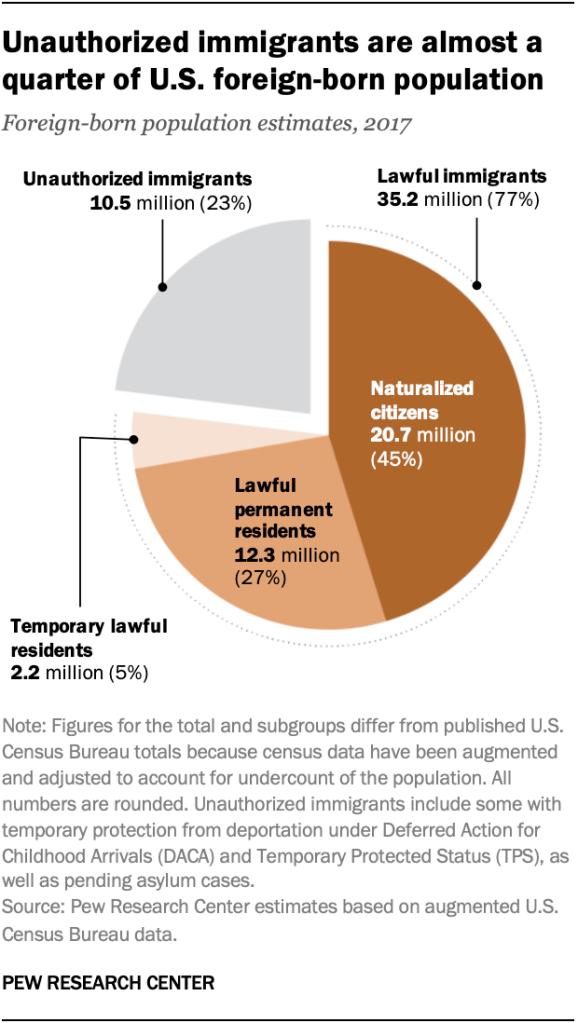
Linguistic characteristics
Half of the immigrants are proficient English speakers. Spanish is the most commonly spoken language among U.S immigrants (followed by English only, Chinese, Hindi, Filipino and French).
Hispanics
Hispanic and Latino are ethnic categories, they are from Spain, Central and South America and the Dominican Republic. They have a unique cultural identity called “Hispanicness”. the Mexican immigration is starting to decline because of the weakening of US job and construction markets; and new laws that reinforce the border between South America and deportations.
Asians Americans
Origins from East Asia, Southeast Asia and South Asia, The 6 largest Asian-American groups : Chinese, Filipinos, Indians, Vietnamese, Koreans and Japanese. Asians earn much more than the average American population. They’re also the best educated group as we said there are also socially assimilated what does that mean it means that they are involved in mixed marriages or they live in mixed neighborhoods.
Americans’ perception on immigration
Americans perception on immigration overall again and according to some surveys and studies a majority of Americans have positive views on immigration they tend to say that immigration strengthens the country because of immigrants hard work because of their talent of course there are some differences of opinions depending on political affiliations the the perspective won’t be the same if you are a Democrat or a Republican there are also different perceptions depending on the immigrant group generally speaking they are quiet positive views of Asians and Europeans and less positive views of African Latin American immigrants that’s reality that’s a fact and also Americans are very divided on future immigration levels almost half of Americans saying that immigrant immigration should be decreased while one third said immigration should be kept at present level and just 15% of them said that immigration should be fixed.
The United Kingdom 🇬🇧
(England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland)
Concept and definitions
- Culture : is the root of the word “multiculturalism”, culture = practices and lifestyle shared by some human beings, always in progress not still, evolving.
- Britishness : to be british, British nationhood came to be ‘added on’ to other identities, Scots, Welsh, English, or more purely local ones, rather than replacing them, or merging with them. Great Britain was ‘an invented nation.’ In this respect being British = multiple identities. national identity carrying the values of the UK
- Multiculturalism : The Oxford English Dictionary offers a broad definition of multiculturalism as the “characteristics of a multicultural society” and “the policy or process whereby the distinctive identities of the cultural groups within such a society are maintained or supported”. complex notion, multiple definitions but about people living together peacefully.
- Assimilation : The images of the melting pot and salad bowl also apply to the UK, even though the expressions themselves are not used. The image of Salad Bowl and Melting pot. Propensity of immigrants to enter a mainstream identity, thus erasing parts of their original culture. Assessed through different criteria such as the access to employment, how well immigrants do in education, if they marry and/or have children, with whom (intermarriages). At the local and national levels, cohesion (in neighbourhoods for example) is also considered.
- Integration : Immigrants do not have to erase their original culture to enter a mainstream identity, a kind of tolerance needed.
Immigrants, by not sharing some ancestral connections, will weaken a sense of British or national identity. -> Fear of a dilution of national identity
Origins of the immigration in the UK
- The British Empire: where the sun never sets
- Started with the conquest of Ireland in the 1580s (Ulster Plantations)
- Then colonies in North America and the West Indies (17th century)
- The East India Company established trading posts in India and China (18th century)
- Australia, Africa and many other colonies were also added to the Empire
- The British Empire: wealth in trade and people
- Trade in products such as cotton, tea, spices, linen, indigo and slaves
- Native populations were put to work or used as slaves in the case of the Africans.
- Some, like the Indians (of India), were enrolled in the British Army
- In India, the local population was used in civil services and education
- The British: a ruling people
- As a consequence of the hegemony of the British Empire, British people have constituted a large network of authority and influence
- Creation of the Commonwealth of Nations as a result of the fall of the Empire in the 20th century 🡺 those nations were the first to send their people to the UK

There are 54 countries in the Commonwealth, in Africa, Asia, the Americas, Europe and the Pacific. Commonwealth countries are diverse – they are amongst the world’s biggest, smallest, richest and poorest countries. 32 of our members are classified as small states. Small states are especially vulnerable to things like climate change or developmental challenges.
Leaders of member countries shape Commonwealth policies and priorities. Every 2 years, they meet to discuss issues affecting the Commonwealth and the wider world at the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM). All members have an equal say regardless of size or wealth. This makes sure even the smallest countries have a voice in shaping the Commonwealth.

- Post WWII immigration history
Different waves of immigration, mainly from former colonies and Legislation had to be implemented to regulate race relations.
- 1950’s : full employement, Caribbean immigration
- 1960’s : Caribbean and African
- 1970’s : Ugandan Asian (Leicester) and Asian (Bradford-Bangladesh)
- 1980’s : Legal immigration flow stopped
- 1990’s : illegal immigration becomes a problem
- 2000’s : economic immigration - temporary - from new eastern European countries
- London
City of London : 7700 people Greater London : 8 817 300 people
Ethnic groups :
- White British (44,9%)
- Other White (14,9%)
- Asian British (18,4%)
- Black British (13,3%)
- Arab British (1,3%)
- Mixed (5%)
- Others (2.2%)
The UK : Difficult race relations
- 1950s-1970s
- From the outside, Commonwealth immigrants were welcome with open arms
- However, discriminations already existed
- What undermined this multicultural society = the disribution of wealth
How did we get there ? From the 1980s onward, race relations coupled with difficult economic conditions have triggered social unrest, which translated into riots in the main British towns.
- RIOTS , 1980-2011
April 1980 – Bristol April 1981 - Brixton, south London July 1981 - Toxteth, Liverpool October 1985 - Broadwater Farm, Tottenham, London March 1990 - Poll tax riots, London May-July 2001 - London May Day riot and violence in northern England August 2011 - London, Manchester and other major cities
Riots are the VISIBLE expression of the ill-being of British society. Riots between 1980 and 2011 had common points :
- about race
- conflicting relation with the police
- poverty
- Race and the police
- Racial confrontation
- Conflict with the police
- A sense of injustice
- Poverty
- arson, looting and attacks on the police
- Working-class estates
- High youth unemployment
- Economic deprivation
- So what about multiculturalism ?
The strategy of multiculturalism has failed to create a common core of values. Is multiculturalism leading to segregation ? Immigrants becoming citizens now have to pass a test on language, culture, and history.
2002 : introduction of the « Life in the UK » test (British citizen test)
African -American Issues
More than half the country’s 41.4 million African Americans lived in the South.
- 21st century
10 Southern states had black populations exceeding 1 million. African Americans were also concentrated in the largest cities, with more than 2 million living in New York City and more than 1 million in Chicago. Detroit, Philadelphia, and Houston each had a black population between 500,000 and 1 million.
** Different processes have led to today’s situation of tense racial relations in the U.S. : **
- The English Empire settling in Africa
- Slavery
- Segregation
- Fight for equality
- Racial discrimination
- Trading Outposts
Until the 17th century, the English were mainly interested in African produces such as pepper, ivory or gold. So they had some sort Rivalry on the West coast of Africa.
- Slavery
- Lifelong status
- Hereditary (for children born of enslaved women)
- Based on race
- Enslaved people were considered as property -> They could be sold, bequeathed, emancipated (freed) sometimes
Slavery started in 1619 (for the English/British Empire). In the 17th century , that was the development of slavery in the American colonies. Slaves were preferred to indetured servants. And in the 18th century, most of the Southern States relied on slavery.
- The Abolition of Slavery
Civil war (1861-1865) between free states (the Union) and the slave states
(the Confederate states).
=> Emancipation Proclamation in 1863
-> Abolition of slavery in 1865 with the 13th Amendment to the American Constitution (A.Lincoln)
- Segregation
Segregation : the action of setting someone aside, in this case, because of race. Even though ex-slaves were free (Abolition of slavery in 1865), they were not considered as equal to the whites. They did not have equal rights. The Jim Crow Laws (1876-1965) denied African-Americans social, economic and political rights : racial segregation.
=> 1896 : Plessy vs Ferguson : racial segregation is constitutional ‘Separate but equal ' doctrine. But Blacks were not granted equal treatment
- The fight for Equality
1909 : creation of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) : a civil rights organization to end legal racial segregation 1954 : Brown v. Board of Education : segregation. in public schools is banned. However, changing the thoughts and attitudes of people in the South was difficult. 1964 : The Civil Rights Act : outlawed discrimination in jobs and public places.
Today, racial discrimination persists.
Immigration in Canada 🇨🇦
Founding people
3 founding peoples in Canada :
- The aboriginal peoples - long before the pioneer arrived in Canada, three majors groups = The Inuit (live in Nunavut) / The first Nations / The Metis
- French Canadians - different communities among these group = the Acadians (french colony) / The Quebecers / the small French-speaking communities across Canada
- British Canadians
Canada’s immigration policy
4 main periods :
- Until the Canadian Confederation :
- before 1763 (The french regime)
- from 1763 to 1867 (during The British regime)
- After Confederation :
- after 1867
- after WWII
I - Until the Canadian Confederation
The French Regime (before 1763) : France had colonized some parts of the new world, the French domination. People that immigrate during that time were all french. Mainly interested in the Fair trade.Very very few immigrants during that time.
The British Domination : After 1763, Treaty of Paris so France decided to give up his territories in the New World so end of the French Colonization. American loyalists remain on the domination of the British to flea the Royal Crown.The beginning of the British Domination.
In the 19th century British and Irish Immigrants still come to immigrate in Canada, The Great Famine, all gather by one thing : English.
II - After Confederation
1867 : creation of the Canada that change the population - major change in the labor (many immigrants where call for building projects). Example : The Canadian Pacific Railway (1881-1885) and Chinese immigrants = a really dangerous construction / High rate of death The Chinese Head Tax that consisted to stop Chinese immigration, only Chinese man (no women or kid), 50$ first but after 500$ and once they paid it they receive a certificate (slide).This piece of legislation was the first based on ethnic race. 🇨🇳
People on Eastern Europe(especially from Ukraine) come to settle in the West of Canada. Those people were attracted because they wanted a new life out of poverty, war, etc… They tented to gather and cluster. This is what lead to the Block Settlements (small colonies in which people would gather together) . Beginning of the preservation of this ethnic diversity. Assimilation was the key word of Canada.
After WWI, people were very suspicious. Nativism revived was still present, especially after The Russian revolution of 1917. People were afraid of being invaded by Communism (The Red Scare). So real slow down immigration in Canada.
III - After World War II
Things started to change due to Canada needed some workers, labor shortage to fill.
In the 1950’s : promotion of Canada’s economic growth : only Europeans were accepted (Italy / Spain / Greece/ Refugees).
Since the 1970’s : things have changed a lot, emergence of visible minorities from the developing world. People can come from almost all the part of the world.
1967 : Immigration Act
The Immigration policy in America were completely revised. Implemented in 1967. These act change everything because it ended racial discrimination as a feature of the Immigration system. These selections is not possible anymore ( racial/national ). From 1967, Immigrants were selected according a system of points, especially according their work skills / their education levels and their language abilities (English/ French).
As a consequence today , they are three main categories of Immigration :
- Economic class : selected according a system of points adapted to the needs of the labor market. ( ex : The Skilled Worker Immigration Program ) Training / Education / Languages , 60%
- Family Class : when someone is sponsored by a relative already living in Canada. (Recommendations/Reunite) 30%
- Refugees Class : 10%, People can apply to have a permanent residence, someone who want to leave his country for many reasons.The most recent were the Syrians in 2016 because of the conflict in Syria. And also many illegals immigrants who crossed the border between USA and Canada.
Ethnic and visible minorities
Definitions :
Ethnic Minorities : People who do not belong to one of the two charters groups or the Aboriginal category and who still retain some elements of their parents or ancestor’s original foreign identity ( language, religion, customs…)
Immigrants : people who have come to Canada to settle but who have not yet acquired Canadian citizenship (recent/established immigrant)
Visible minorities : ‘persons, other than Aboriginal people, who are non-Caucasian in race or non’white in color.’’ (Canadian Employment Equity Act)
According to the last 2016 Census :
- Over 250 ethnic origins reported
- More than 1 in 5 Canadians are foreign-born
- Almost half of the foreign-born population is from Asia
- Africa accounts for the second largest source continent of recent immigrants
- Growth of the visible minority population(22,3% of the population) : South Asians, Chinese and Blacks
- The visible population expected to grow and represent between 31.2% and 35.9% of the Canadian population by 2036.
Historical geographic distribution :
- The prairies : Ukrainians, Germans, Polish
- Ontario : Italians, Chinese, East Indians and Caribbeans
- British Columbia : Chinese
- Quebec : Haitians, Italians
- Atlantic Canada : Europeans
Half of the immigrants live in Toronto, Vancouver and Montreal. The prairies are welcoming more immigrants (job opportunities and high standards of living).
Linguistic and economic integration of ethnic minorities
In 2016, the vast majority of Immigrants, like more than 93% were able to speak in English or French meaning that very very few immigrants are not able to speak one of these two languages. Although, the situation is different in Quebec, because it’s a french speaking province (official language), so more and more french speaking immigrants were selected in this province of Quebec. The majority speak French but outside Quebec the majority speak English.
Social and economic integration :
Knowing one of the 2 official languages help immigrants to be socially and economically integrate.(French in Quebec and English others) Many immigrants considered that the social and economic experience in Canada is the best (high education / work experience / freedom / Human Rights / Safety) but finding a job is very difficult.
But also many immigrants find that finding is probably the most difficult, that’s why many of them have reported unsatisfy economic experience. Different reasons for that :
- a lack of work experience
- the language barrier
- recognition of education / diploma (for example doctors => taxi drivers)
The birth of Multiculturalism
Since the end of the 1960’s, Canada has been a country characterize by ethnic diversity. In 1971, the Canadian Government and especially the Prime Minister of the time (Pierre Eliot Trudeau), officially announced multiculturalism as a policy in order to recognize the cultural contribution of different ethnic groups to Canadian society.
- So in the 1960’s, there was a special commission which was implemented in Canada called “The Royal Commission on Bilingualism and Biculturalism”. The goal of this contribution was to analyze the contribution of others ethnic groups in Canada (the people who were not French Canadian or English Canadian). They decided to give greater recognition to them.
- In 1971, Pierre Eliot Trudeau officially announced a program of “Multiculturalism Within a Bilingual Framework”.
- In 1982, Multiculturalism became a constitutional right, it was especially written down in the chapter 27 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.(Collective rights)
The different meanings of Multiculturalism
- A demographic fact
- An ideology
- A public policy
Purposes of multiculturalism
- to reduce prejudice
- to support and encourage cultural preservation
- to integrate (not to assimilate)
- to promote intergroup contacts and cultural exchanges
- to promote social and economic integration
Evolution of multiculturalism
Multiculturalism was launched 50 years ago, so of course the policy have evolved. In 1988, Multiculturalism became a law with the Canadian Multiculturalism Act meaning that the aim of this law was not just to preserve cultural identity but also to establish legislation to protect ethnic / racial / linguistic / religious diversity in Canada. The main objective was to eliminate racism, so many programs like the “Stop racism” campaign which were developed to address this issue of racism hatred and discrimination. In the 1980’s, Politicians were very worried and aware about this situation of inequality. They were also many employment equity measures implemented to help new comers to help immigrants to get a fair access to employment. Others measures were taken for immigration education for example some initiatives were taken to recognize the history of certain groups by promoting black history for example (Black history month).
The perception of multiculturalism by Canadians
- Immigration has a positive effect on Canada’ (Citizenship and Immigration,2007)
- Positive contribution to the growth of the nation (high educated immigrants)
- Absence/few of illegal immigrants
- Election of Justin Trudeau (Liberal) in 2015
The perception of multiculturalism by Canadians
Canada : 68%(more things to fit) / 32%(encourage cultural diversity)
United States : 53%(more things to fit) / 47%(encourage cultural diversity)